CLASS-6
SUBTRACTION OF INTEGERS
SUBTRACTION OF INTEGERS -
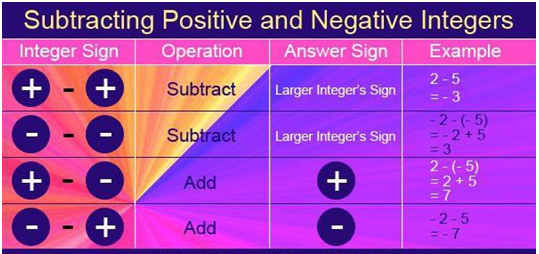
Subtraction of integers involves finding the difference between two integers. It is a fundamental arithmetic operation that follows specific rules based on the signs of the integers being subtracted. Let's explore the rules and examples of subtracting integers:
- Subtracting Positive Integers:- When you subtract a smaller positive integer from a larger positive integer, you simply subtract their numerical values. Example: 8 - 3 = 5
- Subtracting Negative Integers:- When you subtract a negative integer, it's equivalent to adding its positive counterpart. In other words, subtracting a negative is the same as adding a positive. Example: 6 - (-2) = 6 + 2 = 8
- Subtracting Positive and Negative Integers:- Subtracting a negative integer is similar to adding a positive integer. Change the subtraction sign to addition and change the sign of the negative integer to positive. Example: 5 - (-4) = 5 + 4 = 9
- Subtracting from Zero:- Subtracting an integer from zero is the same as adding its additive inverse (its negative counterpart). Example: 0 - 7 = -7
Here are a few more examples to illustrate these concepts:
- 12 - 5 = 7 (Positive - Positive)
- -8 - (-3) = -8 + 3 = -5 (Negative - Negative)
- 10 - (-6) = 10 + 6 = 16 (Positive - Negative)
- -3 - 9 = -3 + (-9) = -12 (Negative - Positive)
- 0 - (-2) = 0 + 2 = 2 (Subtracting from Zero)
When performing subtraction of integers, you can use the number line as a visual aid, just like in integer addition. Moving to the left on the number line represents subtraction. The distance you move corresponds to the absolute value of the integer being subtracted.
Understanding these rules and practicing with examples will help you build a solid foundation in subtracting integers and enhance your overall mathematical skills.