CLASS-5
MULTIPLICATION OF DECIMAL NUMBER
Multiplication of Decimal Numbers
Multiplication of decimal number is required for the measuring purpose of length, width of the land, finding distance or measurement of cloths and so on. By multiplication of decimal numbers we can solve out the complex calculations which are very much required for measurement of area and house building and decimal multiplication calculation is very effective for solving chemical & physics related equations also.
Example.1) 3.2 x 15 = ?
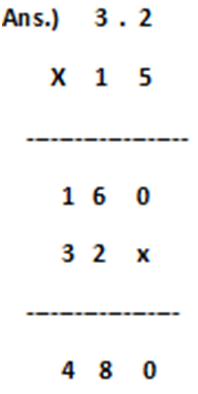
Step.1) Multiply these two numbers by considering both numbers are as a whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Step.2) Count the number of decimal places for both the number ‘Multiplicand’ and ‘Multiplier’ and add the number of decimal places ( 3.2 = 1 decimal places and 15 = 0 or nil decimal places; so, total decimal places are 1 + 0 = 1 decimal place )
Step.3) Put the decimal point in the product from the right, after as many digits as the total number of decimal places is obtained from ‘Multiplicand’ and ‘Multiplier’. So, the answer is 48.0 (one decimal place as obtained from both the Number ‘Multiplicand’ and ‘Multiplier’).
Example.2) 2.12 x 2.5 = ?

Step.1) Multiply these two numbers by considering both numbers are as a whole numbers ignoring the decimal point.
Step.2) Count the number of decimal places for both the number ‘Multiplicand’ and ‘Multiplier’ and add the number of decimal places ( 2.12 = 2 decimal places and 2.5 = 1 decimal places; so, total decimal places are 2 + 1 = 3 decimal places )
Step.3) Put the decimal point in the product from the right, after as many digits as the total number of decimal places is obtained from ‘Multiplicand’ and ‘Multiplier’. So, the answer is 5.300 (three decimal places as obtained from both the number ‘Multiplicand’ and ‘Multiplier’).
Important Fact about Decimal Multiplication
1) On multiplying a decimal by 10, the decimal point moves one place to the right.
2) On multiplying a decimal by 100, the decimal point moves two places to the right.
3) On multiplying a decimal by 1000, the decimal point moves three places to the right.
4) On multiplying a decimal by 10000, the decimal point moves four places to the right.
5) On multiplying a decimal by 100000, the decimal point moves five places to the right. Continues……..
6) Multiplication of any decimal number with zero ‘0’, the product always must be zero ‘0’.
7) Multiplication of any decimal number with 1, the product always must be the same number itself.